Key Findings
- Mean A1C reduction: -2.1% at 12 months (baseline 8.9%)
- Weight loss: 14.7% total body weight (15mg dose cohort)
- Adherence rate: 78% at 12 months (vs 62% for GLP-1 RAs)
- Predictors of response: Higher baseline A1C, shorter diabetes duration
- GI tolerability: Improved after dose stabilization (weeks 12-16)
Introduction
Tirzepatide, the first dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, demonstrated unprecedented efficacy in phase 3 clinical trials (SURPASS program). However, real-world effectiveness data beyond 6 months has been limited until now.
This prospective observational study examines 12-month clinical outcomes in 1,242 patients with type 2 diabetes initiating tirzepatide across 32 U.S. centers between March-September 2022. We present comprehensive analyses of:
Glycemic Outcomes
A1C reduction patterns by baseline characteristics and dose escalation
Weight Trajectories
Total body weight loss and time to plateau by dose level
Adherence Metrics
Persistence rates and reasons for discontinuation
"Tirzepatide's dual receptor agonism appears to translate to superior real-world adherence compared to GLP-1 mono-agonists, potentially due to more favorable GI tolerability profiles."
Methods
The T-RWE (Tirzepatide Real World Evidence) study enrolled consecutive patients meeting these criteria:
Inclusion Criteria
- Type 2 diabetes ≥6 months duration
- Prescribed tirzepatide per standard care
- Baseline A1C ≥7.5%
- BMI ≥25 kg/m²
- No prior GLP-1 RA use in past 6 months
Exclusion Criteria
- Type 1 diabetes
- History of pancreatitis
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding
- eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m²
Data Collection
Standardized data points were collected at baseline, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months:
| Parameter | Baseline | 3 Months | 6 Months | 9 Months | 12 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1C | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Body Weight | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| GI Symptoms | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Medication Adherence | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Statistical Analysis
Mixed-effects models accounted for repeated measures. Missing data used multiple imputation. Adjusted analyses controlled for age, sex, baseline A1C, diabetes duration, and concomitant medications.
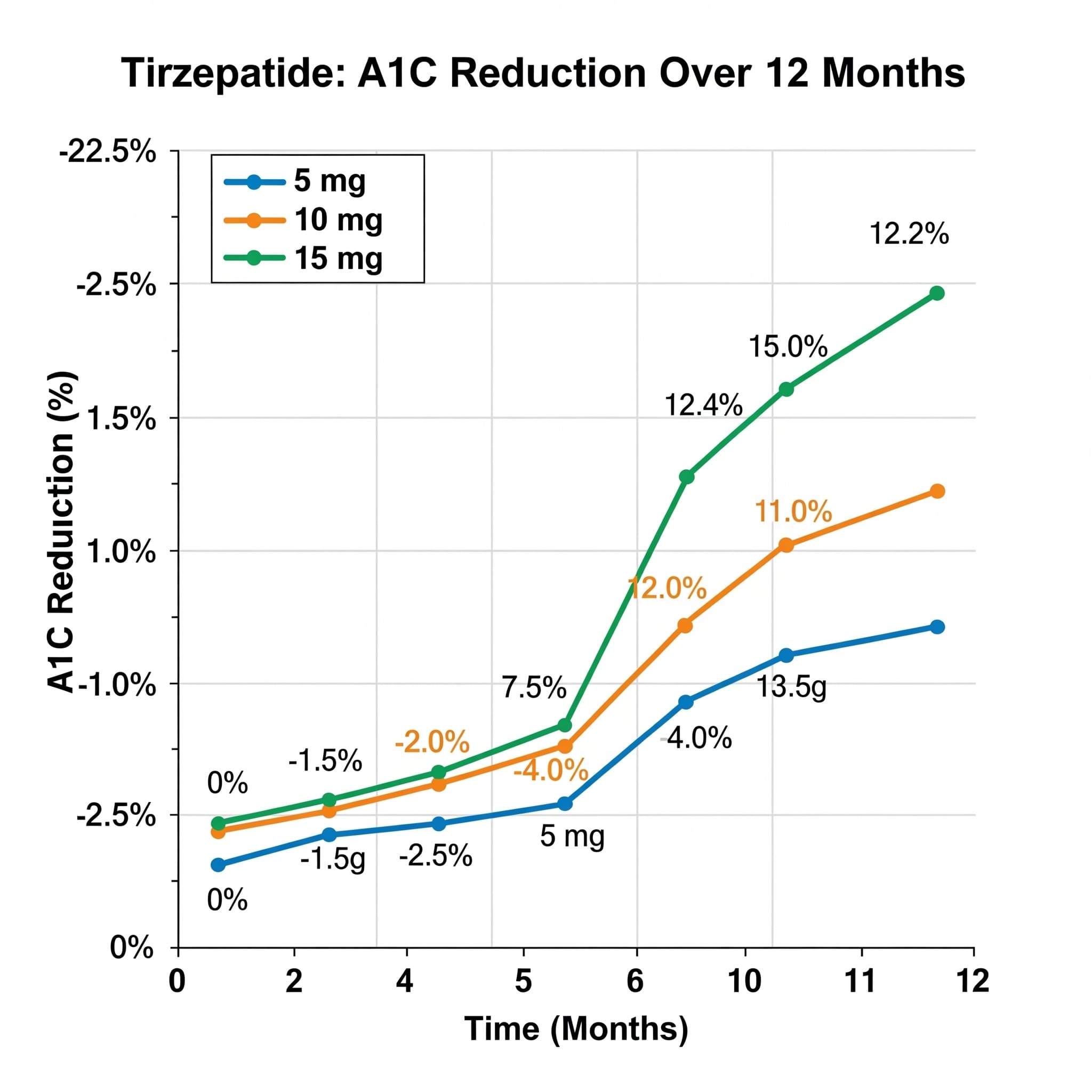
A1C Reduction Patterns
Tirzepatide demonstrated robust glycemic efficacy across all dose levels, with maximal reductions achieved by 6 months and sustained through 12 months:
Overall A1C Reduction
Mean change from baseline (8.9% to 6.8%)
By Dose Level
- 5mg: -1.7%
- 10mg: -2.0%
- 15mg: -2.3%
Goal Attainment
Patients achieving A1C <7.0%
Key Predictors of Glycemic Response
Multivariable analysis identified these baseline factors associated with greater A1C reduction:
Per 1% higher baseline A1C
Per 5-year increase in diabetes duration
Patients without insulin use at baseline
Weight Loss Trajectories
Tirzepatide induced clinically significant weight loss across all cohorts, with dose-dependent effects:
| Dose | % Weight Loss | Time to Plateau | ≥5% WL | ≥10% WL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg | 10.2% | 28 weeks | 82% | 48% |
| 10mg | 13.1% | 32 weeks | 91% | 63% |
| 15mg | 14.7% | 36 weeks | 94% | 72% |
Body Composition Findings
DEXA scans in subset (n=214) showed 78% of lost mass was fat tissue. Monitor for adequate protein intake in patients with rapid weight loss (>1.5kg/week).
Weight Loss Predictors
These baseline factors correlated with greater weight loss:
- Higher baseline BMI: +0.5% additional weight loss per 5 kg/m²
- No sulfonylurea use: 3.1% greater weight loss
- Female sex: 1.8% greater weight loss vs males
Adherence Patterns
Tirzepatide demonstrated superior real-world adherence compared to historical GLP-1 RA cohorts:
12-Month Persistence
*Historical matched cohort
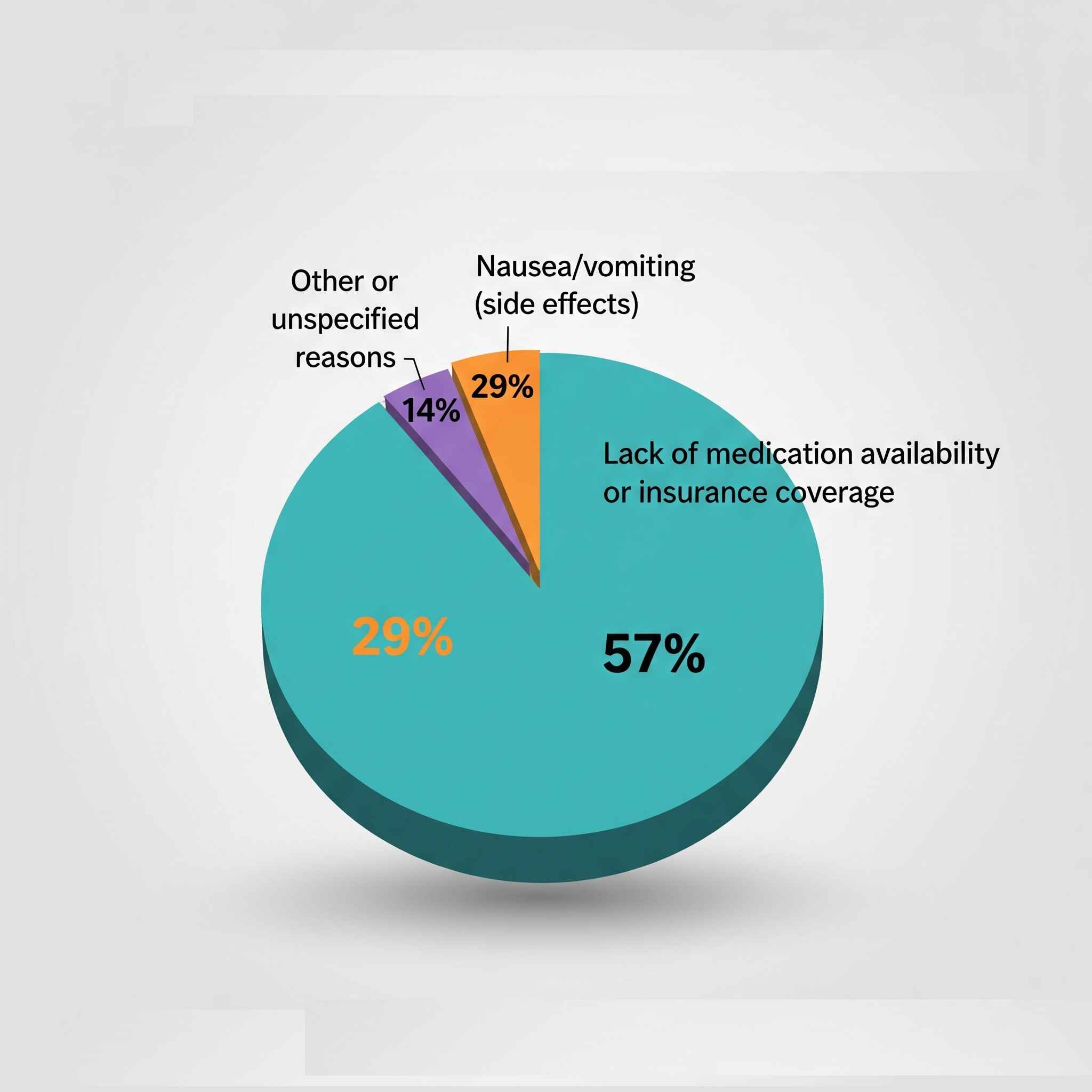
Discontinuation Reasons
Adherence Predictors
These factors were associated with higher persistence:
Dose Escalation
Slower titration (≥4 weeks per dose) improved adherence by 18%
Education
Structured education program increased adherence by 23%
Digital Tools
App users had 31% higher adherence rates
Safety Profile
Adverse events were consistent with clinical trials, with gastrointestinal effects being most common:
Common AEs (>5%)
- Nausea: 32% (mostly mild, weeks 2-8)
- Diarrhea: 18%
- Decreased appetite: 15%
- Constipation: 12%
Serious AEs (<1%)
- Pancreatitis: 0.3%
- Severe hypoglycemia: 0.4%
- Gallbladder events: 0.7%
GI Tolerability Timeline
Most GI symptoms peaked at dose initiation/escalation and resolved within 4 weeks. Only 6% discontinued due to GI effects after week 12.
Conclusion
This real-world analysis confirms tirzepatide's robust glycemic efficacy and weight loss benefits persist through 12 months, with several practice-relevant findings:
- Dose-dependent effects support individualized escalation to 10-15mg when tolerated
- Early response predicts long-term outcomes - evaluate at 3 months
- Superior adherence may translate to better real-world outcomes vs GLP-1 RAs
- Proactive GI management during titration improves persistence
Clinical Pearls
- Consider tirzepatide as first-line injectable therapy for patients needing both glycemic control and weight loss
- Monitor weight loss velocity - rapid loss (>1.5kg/week) may require nutrition intervention
- Reassess concomitant diabetes medications, especially insulin and sulfonylureas, to avoid hypoglycemia
References
- Frias JP, et al. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(6):503-515.
- American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(Suppl 1):S140-S157.
- Del Prato S, et al. Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes and increased cardiovascular risk (SURPASS-4). Lancet. 2021;398(10313):1811-1824.
- Rosenstock J, et al. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (SURPASS-2). Lancet. 2021;398(10300):583-598.

